Calcaneal Fracture Diagnostic Aid System
I am mainly responsible for the design of the overall framework of the software and the training of deep learning models.
I produced a paper that is now UNDER REVIEW and the abstract is:
Fracture diagnosis is critical in clinical settings, and imaging modalities like X-ray and CT scans are crucial for bone fracture diagnosis. Although X-ray scans are more convenient and affordable, however, X-ray scans are prone to misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis due to the limited number of poses that can be observed and the uneven distribution of grayscales. Deep learning methods show great potential in improving the efficiency and accuracy of x-ray fracture diagnosis.
This paper proposes MTL-DlinkNet, a multi-task learning model based on DlinkNet, that can perform both classification tasks for automatic identification of calcaneus fractures, and segmentation tasks for generation of regions of interest (RoI). The model achieves high accuracy (0.989 AUC) while annotating the data at the same time, making diagnosis more efficient and reducing the burden on doctors. The paper also presents an intelligent diagnostic tool for calcaneus fracture that assists doctors in clinical settings. The main contributions of this work include building a dataset of foot X-rays for fracture diagnosis, proposing a better-performing fracture diagnosis deep learning model, and developing an efficient diagnostic tool. Experimental results show that the MTL-DlinkNet model achieves better performance than the baseline models.
Overall, this paper demonstrates the potential of deep learning methods in improving fracture diagnosis accuracy and efficiency, with practical applications in clinical settings.
The overall flow of using the software is shown in the figure:
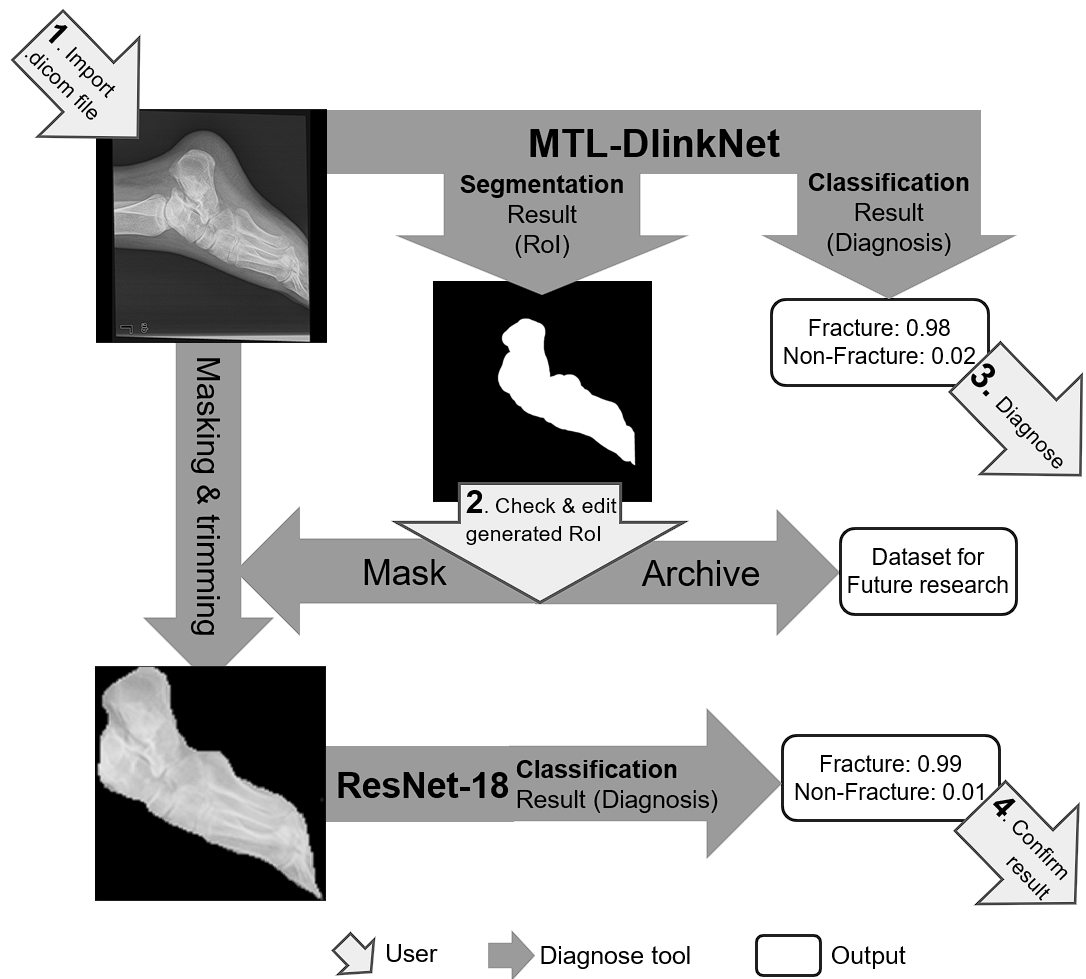
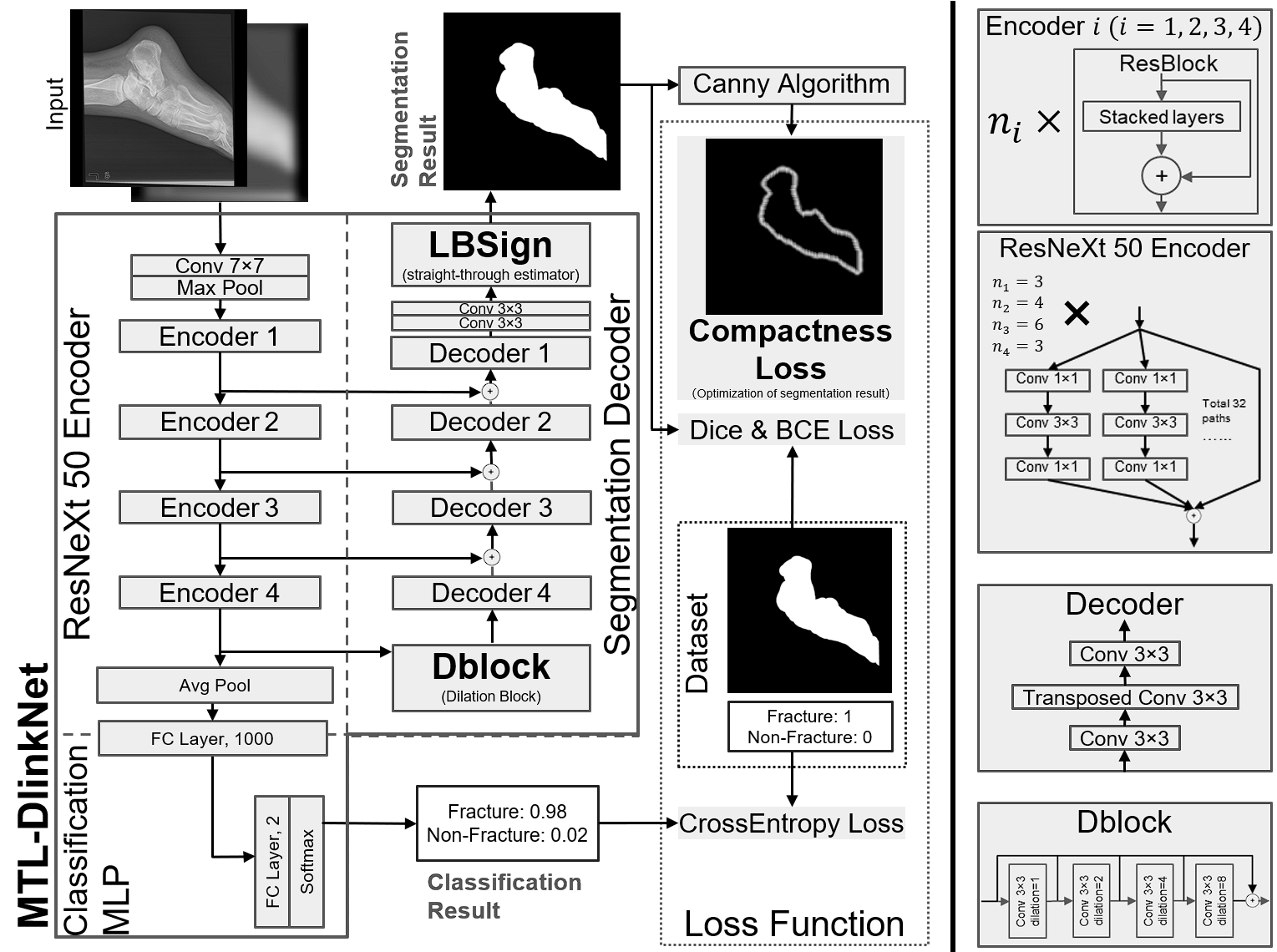
Among these MTL-DlinkNet is shown in the figure below:
Our team won the first prize of Feng Ru Cup in school and the third prize of Internet+ Beijing Competition.
